Introduction to Ecotourism: Principles and Practices

In today’s world, where environmental degradation and climate change are pressing concerns, ecotourism emerges as a sustainable approach to travel that balances the desire to explore with the need to preserve. Ecotourism is a form of responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of local people, and involves interpretation and education.
What is Ecotourism?
Ecotourism goes beyond simply visiting scenic spots. It is about experiencing nature in a way that respects the environment and local cultures. The goal is to create awareness among tourists about environmental issues while supporting conservation efforts and local economies. Unlike conventional tourism, which often results in environmental harm and cultural disruption, ecotourism strives to minimize negative impacts.
Core Principles of Ecotourism
Minimize Environmental Impact: Ecotourism promotes practices that reduce waste, pollution, and resource depletion. This includes using eco-friendly transportation, supporting renewable energy, and adhering to ‘leave no trace’ principles.
Build Environmental and Cultural Awareness: Tourists are encouraged to learn about the ecosystems, wildlife, and cultures they encounter. Education is a key aspect of ecotourism, helping travelers understand their role in conservation.
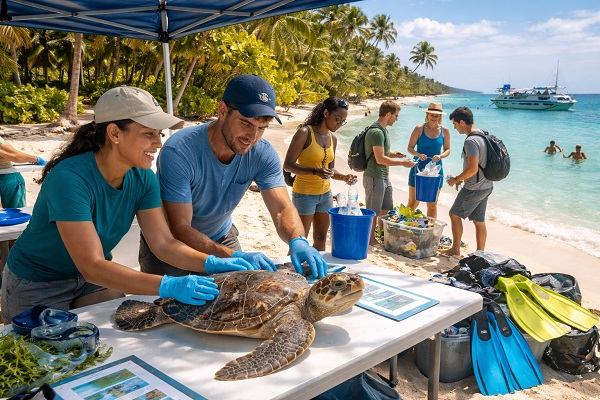
Support Conservation Efforts: Revenue from ecotourism often contributes directly to protecting natural areas and wildlife. This financial support can fund conservation projects and park maintenance.
Benefit Local Communities: Ecotourism emphasizes empowering local people by involving them in tourism activities, providing employment, and encouraging the use of local products and services. This fosters sustainable livelihoods.
Respect for Local Cultures: Tourists are encouraged to appreciate and respect the traditions and lifestyles of indigenous and local communities without causing disruption.
Practices in Ecotourism
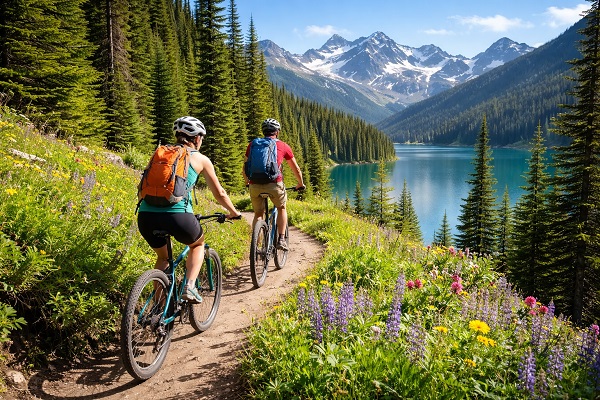
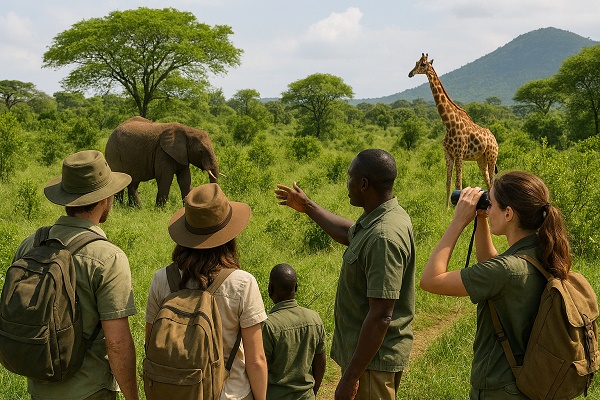
Guided Nature Tours: Experienced guides lead small groups through natural habitats, providing insightful knowledge while ensuring minimal disturbance.
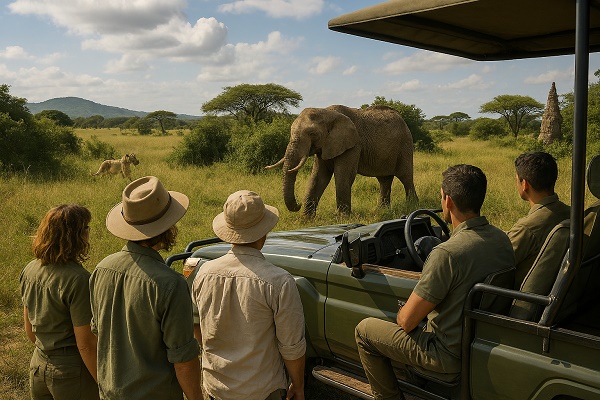
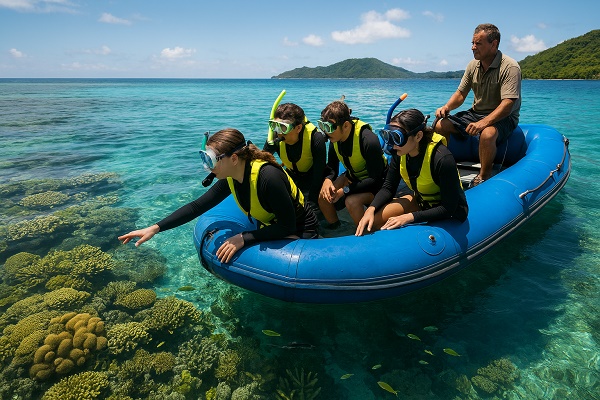
Wildlife Observation: Viewing animals in their natural environment without interfering with their behavior.
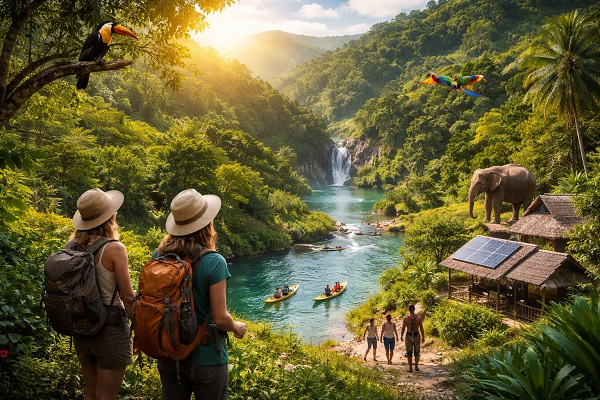
Community-Based Tourism: Tourists engage with local communities through homestays, cultural events, and crafts, directly benefiting the locals.
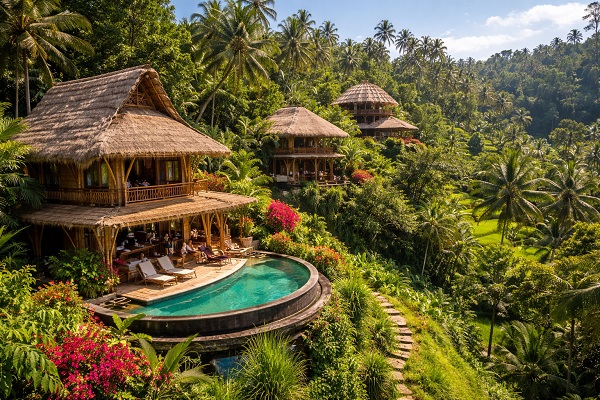
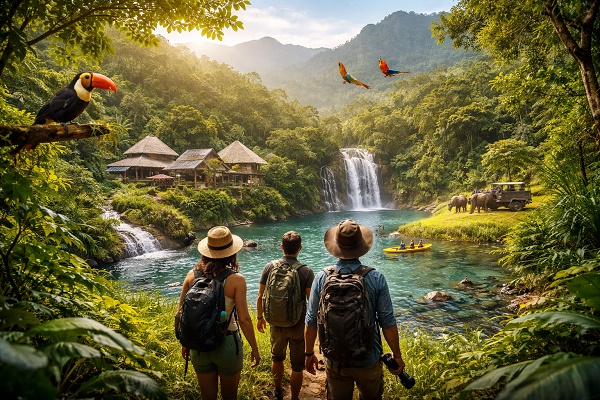
Sustainable Accommodation: Eco-lodges and green hotels utilize sustainable materials and energy sources, reducing their environmental footprint.
Environmental Education Programs: Workshops and activities educate visitors on conservation issues and responsible behaviors.
The Growing Importance of Ecotourism
With increasing awareness about environmental challenges, ecotourism has gained momentum globally. It offers a way to travel consciously, preserving the planet’s beauty for future generations. However, successful ecotourism requires commitment from travelers, businesses, and governments alike to uphold its principles.
By choosing ecotourism, travelers can enjoy enriching experiences while making a positive impact—turning every journey into a step toward a sustainable future.