Zinc Long Term Report 24th Sept 2025 by Kedia Advisory

Strengths
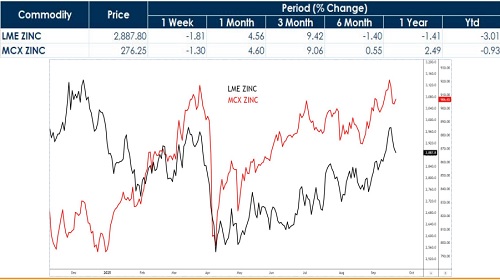
* Zinc climbed over 4.50% in a month tracking LME above $3,000, hitting a near 10-month high.
* The dollar index fell toward 97, hitting an over two-month low ahead Fed rate cut decision.
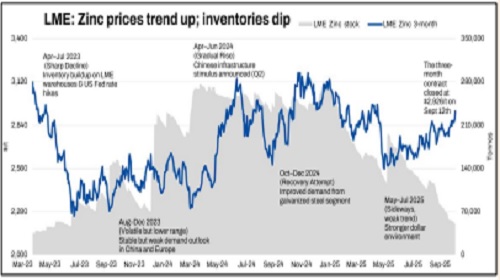
* LME warehouse stocks fall nearly 75% since mid-April to 50,150 tons.
* China’s factory activity in August expanded at the quickest pace in five months to 50.5 on the back of rising new orders.
* The global zinc market to a deficit of 12,000 metric tons in June– ILZSG
* Industrial production in the Euro Area inched higher by 0.3% from the previous month in July of 2025, trimming the revised 0.6% drop in the earlier period
Weakness
* Gains on metals markets were restrained by worries about US tariffs, which helped to dampen factory activity in parts of Asia.
* In August, refined zinc production in China increased over 3% MoM and around 28% YoY.
* ILZSG data show that the global refined zinc market recorded a surplus of 47,000 tons during the first half of 2025.
* China’s Industrial production in August fell to a one-year low, while retail sales slowed to an eight-month low.
* Zinc inventories in warehouses monitored by the Shanghai Futures Exchange rose 8.8% from last Friday
Opportunities
* China’s GDP growth target was set at 5%, and is implementing stimulus measures to boost the economy.
* Zinc supply is tightening as Chinese smelters face pressure to cut production due to capacity outpacing demand.
* Australian smelter Nyrstar announced it would cut this year's output by 25%.
* Ratings agency S&P Global affirmed China’s long-term, short-term, and local currency sovereign credit rating at A+, citing strong fiscal stimulus.
* China is expected to reduce output following Beijing’s renewed efforts to curb overcapacity in key industrial sectors.
* As per daily chart, Golden Crossover is seen (50 MA crossing above 200 MA
Threats
* China’s economy continues to face multiple risks and challenges, citing August 2025’s weak performance amid mounting global headwinds.
* New export orders in China declined for a fourth consecutive month, while falling production led factories to cut jobs during the period.
* China’s production expected to increases in Hunan, Shaanxi, Gansu, Inner Mongolia, and Hubei.
* The global refined zinc market will be in surplus this year – ILZSG
* As per daily chart, RSI showing prices in overbought zone.
Zinc Prices Surge on Supply Tightness
Zinc climbed 4.50% in September, surpassing $3,000/ton on the LME to hit a near 10-month high. Gains were driven by a sharp supply squeeze, as LME inventories collapsed 75% since mid-April to just 50,150 tons, while Australian smelter Nyrstar announced a 25% output cut. Additional momentum came from a weaker dollar index at 97, supporting investor appetite for base metals. China’s factory PMI also expanded to 50.5 in August, the quickest pace in five months, raising optimism for industrial demand. Despite these bullish factors, prices now trade in technically overbought territory (RSI), cautioning traders of possible short-term corrections.
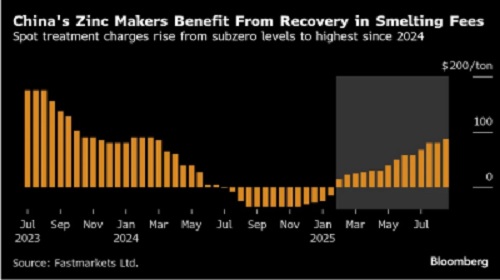
China’s Zinc Smelters Gain Advantage Amid Global Supply Cuts
China’s zinc producers are strengthening their position in global markets as overseas smelter closures tighten supply. Spot treatment charges (TCs) for zinc concentrate delivered to China — a key measure of smelter profitability — have risen sharply, reaching their highest level in more than 18 months after starting the year in subzero territory. This surge reflects tightening global concentrate supply, with production cuts in Japan and Australia reducing export availability. China’s smelters, benefiting from these disruptions, are negotiating better supply terms from overseas miners, consolidating their grip on global zinc refining. The trend underscores China’s growing leverage in the international zinc market
Mixed Signals From China’s Economy
China’s economy showed both resilience and weakness in August. On the positive side, the factory PMI rose to 50.5, supported by new orders, and the government reaffirmed a 5% GDP growth target backed by fiscal stimulus. Ratings agency S&P maintained China’s A+ rating, citing policy support. However, industrial production hit a one-year low, retail sales slowed to an eight-month low, and new export orders fell for the fourth consecutive month. Weak consumption and job cuts in factories underscored fragile domestic demand. This divergence complicates zinc’s outlook: structural policy support provides stability, but weak end-use demand tempers immediate price momentum.
Zinc Inventories Hit 27-Month Low Amid Global Tightness
As of September 10, 2025, LME zinc inventories dropped to nearly 50,000 tons, their lowest since June 2023, after plunging almost 36.8% (29,600 tons) in the past month. The LME 0-3 premium widened to $23.01/ton, reflecting tight near-term supply. In contrast, Shanghai Futures Exchange (SHFE) inventories climbed 8.8% WoW, highlighting persistent domestic surplus as Chinese refined zinc output surged 28% YoY in August. This stark divergence between falling global stocks and rising Chinese reserves underscores a split market narrative — international prices gain support from scarcity, while China’s oversupply continues to cap SHFE zinc momentum
Zinc News
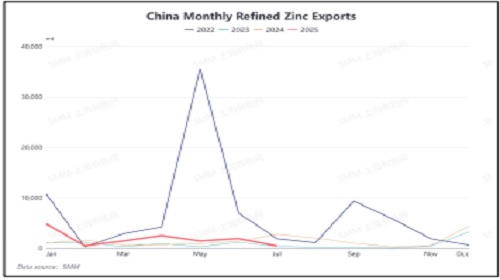
China’s Zinc Export Window Remains Shut Despite LME Squeeze
As of September 10, 2025, LME zinc inventory plunged to 50,000 mt, the lowest since June 2023, with the 0-3 premium expanding to $23.01/mt. While LME prices strengthened on squeeze risks, domestic zinc inventories continued accumulating, keeping SHFE zinc weak under surplus logic. The SHFE/LME price ratio slipped to 7.6, narrowing China’s import losses to 2,500 yuan/mt, while exports still incur losses of 1,000 yuan/mt. Historically, China’s zinc export window only opened in 2022, with monthly net exports peaking at 32,300 mt and annual exports of 80,900 mt. Unless import losses widen toward 4,000 yuan/mt, the export window is unlikely to reopen soon
Macro Tailwinds Support Metals Rally
Zinc’s rally has been reinforced by supportive macroeconomic conditions. The U.S. dollar index fell toward 97, its lowest in over two months, ahead of the Federal Reserve’s expected rate cut, boosting investor flows into commodities. This coincided with broader optimism that stimulus in China will stabilize industrial metals demand. Despite tariffs dampening some Asian factory activity, sentiment toward base metals remains constructive. LME zinc’s 0-3 premium expanded to $23.01/ton, reflecting squeeze risks amid low inventories. These macro drivers, when combined with supply-side stress, sustain zinc’s bullish momentum in the near term, though overbought technical signals point to potential volatility
Global Supply Adjustments Shape Market Balance
The zinc market is in flux as global producers adjust to tightening conditions. Beyond China’s rising output, Beijing has renewed efforts to curb overcapacity, signaling possible future reductions. Internationally, smelters face significant pressure: Nyrstar cut output by 25% in Australia, while other smelters in Japan scaled back due to cost constraints. These supply disruptions offset the ILZSG’s surplus view for 2025, creating localized deficits that drive LME volatility. Spot treatment charges for zinc concentrate have risen sharply, boosting Chinese smelter profitability and underscoring their negotiating power. The market remains finely balanced, with supply disruptions abroad colliding with rising Chinese output.
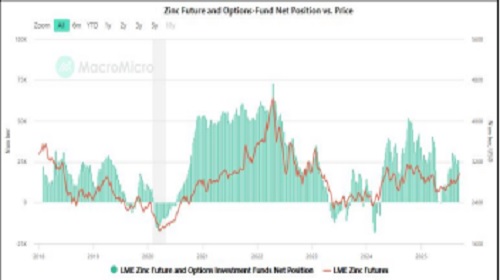
Zinc Funds Rebuild Longs As Prices Hold Above $3,000
As of 2025, LME zinc futures and options net fund positions have climbed back toward 40,000–50,000 contracts, their strongest level since mid-2022. This resurgence coincides with zinc prices stabilizing above $3,000/ton, supported by tightening global supply and shrinking LME inventories. Compared to the heavy liquidations in 2023, current positioning highlights a decisive return of speculative confidence. The rebound mirrors broader commodity inflows following a weaker U.S. dollar index at 97 and China’s industrial stimulus push. However, with zinc already up 4.5% in September and technicals showing overbought momentum, elevated fund exposure could amplify volatility if macro sentiment or Chinese output trends shift.
* According to preliminary data recently compiled by the ILZSG, the global market for refined zinc metal was in surplus by 47kt over the first half of 2025 with total reported inventories decreasing by 109kt.
* Despite reductions in Brazil and the United States, world zinc mine production rose by 6.3%, influenced by increases in Australia, China, Mexico, Peru, South Africa and the Democratic Republic of Congo, where the new Kipushi mine was commissioned in June 2024. Output in Europe also rose, benefiting from higher production at the Vares operation in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the commissioning of the Ozernoye mine in the Russian Federation in September 2024 and the resumption of operations at the Tara mine in Ireland in October 2024.
* Refined metal production fell by 2.1%. This was mainly the result of declines in Brazil, Kazakhstan and Japan, due to the closure of Toho Zinc’s Anakka operation. Production also fell in the Republic of Korea, mainly as a result of a temporary suspension of operations at the Seokpo smelter. These reductions were partially balanced by rises in Peru and Europe, where Boliden recently completed an expansion at its Odda Smelter.
* Increases in the usage of refined zinc metal in China, India and Europe were partially offset by reductions in Brazil and the United States, resulting in an overall global rise of 0.9%.
* Chinese imports of zinc contained in zinc concentrates fell by 48.3% to 1215kt. Net imports of refined zinc metal totalled 180kt, a decrease of 36kt compared to the first half of 2024
Above views are of the author and not of the website kindly read disclaimer