The Lifestyle of Wild Animals
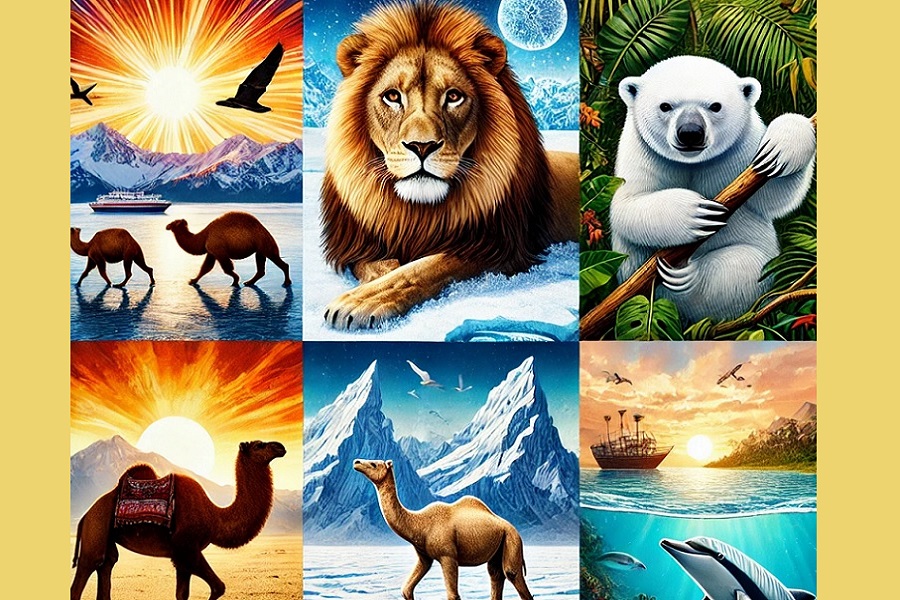

Wild animals lead diverse and fascinating lives, each adapted to its environment in unique ways. The lifestyle of wild animals is heavily influenced by their habitat, food availability, behaviors, and survival strategies. Here’s an exploration of the lifestyles of wild animals across different ecosystems.
1. Savanna and Grasslands
In regions like Africa’s savannas and the grasslands of Asia, animals such as lions, elephants, and zebras roam vast open spaces. These areas are characterized by seasonal rainfall, which impacts the availability of food. Grazing herbivores like zebras and antelopes thrive on grasses, while carnivores like lions rely on hunting to survive. Elephants, as massive herbivores, spend most of their time feeding on trees and grasses, with their herds led by matriarchs.
*Lion: Lions are social creatures, living in prides that consist of related females, their offspring, and a few males. Their lifestyle is built around hunting in groups, usually at night, to catch large prey such as buffalo or wildebeest.
*Elephant: Elephants are highly intelligent and travel in family groups led by the oldest female. Their lifestyle is centered around finding water sources and food. Elephants also play a crucial role in shaping the environment, such as by creating paths that other animals follow.
2. Rainforests
The dense, wet environments of rainforests are home to a rich variety of species. Monkeys, jaguars, toucans, and sloths are among the many animals adapted to the complex layers of the forest. Rainforests are teeming with life, offering abundant food and shelter, but also require animals to be highly adaptable.
*Jaguar: Jaguars are solitary hunters and thrive in the dense forest canopy and on the ground. Their lifestyle revolves around hunting alone, preying on a variety of animals like deer, peccaries, and even caimans.
*Sloth: Known for their slow-moving nature, sloths spend most of their time in the treetops. Their lifestyle involves minimal movement, conserving energy as they feed on leaves and occasionally venture down to the ground to defecate.
3. Arctic Regions
In the cold, icy conditions of the Arctic, animals such as polar bears, seals, and arctic foxes have evolved to survive extreme temperatures. The primary challenge for Arctic animals is finding food, as the winters are long, and the environment is harsh.
*Polar Bear: Polar bears are solitary animals that rely on sea ice to hunt for seals. Their thick fur and a layer of fat help them stay warm. They are excellent swimmers and spend much of their time on ice floes in search of food.
*Arctic Fox: The Arctic fox has a thick coat of fur that changes color with the seasons, offering camouflage in both winter snow and summer tundra. Their diet mainly consists of small mammals and birds, and they are highly adapted to the cold climate.
4. Deserts
Desert animals, such as camels, snakes, and lizards, have developed unique survival strategies to cope with the extreme heat and lack of water. Their lifestyles revolve around conserving moisture and avoiding the hottest parts of the day.
*Camel: Camels are the quintessential desert survivors. Their lifestyle includes long-distance travel in search of water and food, often crossing vast stretches without much sustenance. Their ability to store water and tolerate high temperatures makes them ideal for desert life.
*Fennec Fox: The fennec fox, with its large ears and small size, has adapted to the desert by being nocturnal. This behavior helps it avoid the scorching daytime heat while foraging for food such as insects, small mammals, and plants during the cooler night hours.
5. Ocean and Marine Life
Marine animals, such as dolphins, sharks, and sea turtles, lead dynamic lifestyles that involve migration, hunting, and complex social interactions. Oceans provide a different set of challenges, such as the need to adapt to saltwater, the depth of the water, and the currents.
*Dolphins: Dolphins are highly social creatures, living in pods where complex communication and cooperation are key. Their lifestyle revolves around hunting fish, and they engage in playful behaviors that strengthen social bonds.
*Sharks: Sharks are solitary predators that rely on their keen senses to hunt. They typically roam vast distances in search of food, including fish and seals. Many species of sharks migrate seasonally, following the availability of prey.
Conclusion
The lifestyles of wild animals are varied and intricately connected to their environments. Whether it's the complex social structure of lions in the savanna, the solitary hunting of jaguars in the rainforest, or the survival strategies of polar bears in the Arctic, wild animals are perfectly adapted to their habitats. Their survival depends on the availability of food, the protection offered by their habitats, and the ability to overcome challenges posed by nature.