Biometric Gadgets: Fingerprint, Face, and Beyond
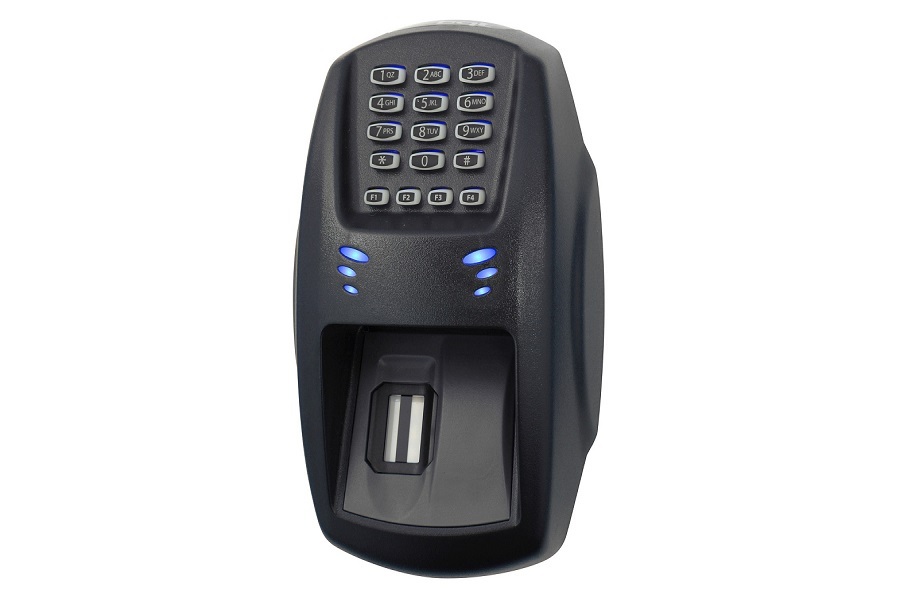

In today’s world, security and convenience are paramount. From unlocking our smartphones to accessing sensitive data, gadgets are becoming smarter at recognizing us. Biometric gadgets, which rely on unique human characteristics such as fingerprints, facial features, and even voice, have revolutionized how we interact with technology.
What Are Biometric Gadgets?
Biometric gadgets use biological traits to identify or authenticate individuals. Unlike traditional passwords or PINs, biometric systems offer higher accuracy and are harder to replicate. This technology is now embedded in smartphones, laptops, smart home devices, and even wearables, ensuring secure and seamless user experiences.
Common Types of Biometric Gadgets
Fingerprint Sensors
Fingerprint recognition remains the most widely used biometric technology. Modern smartphones, laptops, and even office access systems use fingerprint sensors to authenticate users quickly. Some devices now use ultrasonic or optical fingerprint scanning, providing faster and more secure recognition.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology scans your facial features and matches them with stored data. It is commonly used in smartphones, security cameras, and even payment systems. Advanced face recognition can detect depth, contours, and micro-expressions, making it highly secure.
Iris and Retina Scanners
These scanners identify individuals by analyzing the unique patterns in the eye. Iris recognition is extremely accurate and is often used in high-security environments such as airports and government buildings.
Voice Recognition
Voice biometrics analyze your speech patterns to authenticate identity. It is increasingly used in virtual assistants, call centers, and smart home devices for hands-free security.
Behavioral Biometrics
Beyond physical traits, some gadgets analyze patterns in behavior, like typing rhythm, walking gait, or touchscreen gestures. These subtle cues add another layer of security without extra effort from the user.
Applications in Everyday Life
Smartphones and Laptops: Unlock devices, authorize payments, and access apps.
Smart Homes: Control smart locks, security cameras, and home automation systems.
Workplaces: Secure access to offices, servers, and confidential documents.
Healthcare: Protect sensitive medical records while ensuring quick access for authorized personnel.
Banking and Payments: Enable contactless authentication for transactions.
Advantages of Biometric Gadgets
Enhanced Security: Harder to hack compared to traditional passwords.
Convenience: Quick access without remembering multiple passwords.
Personalization: Gadgets can adapt settings and preferences based on the authenticated user.
Challenges and Considerations
While biometric technology is advanced, it comes with challenges:
Privacy Concerns: Biometric data is sensitive and needs secure storage.
False Positives/Negatives: Environmental factors or physical changes can sometimes affect recognition.
Cost: Advanced biometric gadgets are often more expensive than traditional devices.
The Future of Biometric Gadgets
Biometric gadgets are evolving rapidly. Future devices may combine multiple biometrics, like fingerprint + facial recognition, for multi-factor authentication. Emerging technologies like vein pattern recognition and DNA-based authentication could make security even more precise. As AI and machine learning improve, gadgets will become smarter, faster, and more secure in recognizing users.
Conclusion:
Biometric gadgets are no longer a luxury—they are becoming an integral part of everyday life. From fingerprint scanners to facial recognition and beyond, these devices offer unparalleled security and convenience. As technology advances, our interactions with gadgets will continue to become more personal, seamless, and secure.