``The Rise of Telemedicine: How Virtual Healthcare is Revolutionizing Medical Treatment``
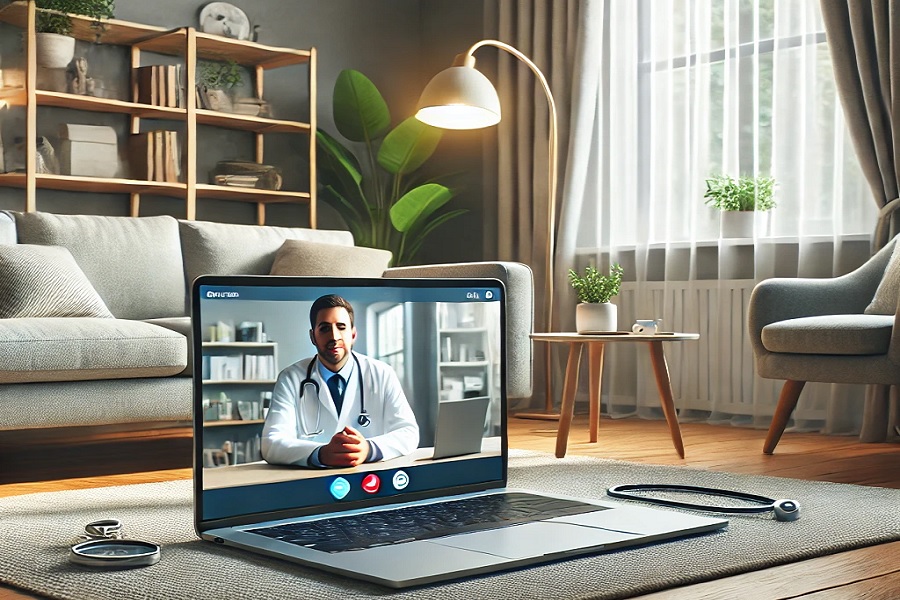

Introduction: Telemedicine, or virtual healthcare, has seen an unprecedented rise in recent years, driven by advancements in technology, increased access to the internet, and the global push for safer, more efficient healthcare delivery. This digital transformation in healthcare allows patients to consult with doctors, receive diagnoses, and even access prescriptions from the comfort of their homes. With its convenience, cost-effectiveness, and potential to address healthcare disparities, telemedicine is reshaping the way healthcare is delivered, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. In this article, we will explore how telemedicine is transforming the healthcare landscape, the benefits it offers, the challenges it faces, and its future potential.
1. The Growth of Telemedicine: Telemedicine has been around for decades, but its widespread adoption accelerated rapidly during the COVID-19 pandemic. With lockdowns in place and social distancing measures preventing in-person consultations, both patients and healthcare providers turned to virtual care to maintain continuity of care. In fact, the global telemedicine market is expected to grow at an annual rate of over 16% in the coming years. Factors such as advancements in video conferencing technology, secure communication platforms, and the expansion of internet access are making telemedicine more feasible and effective.
2. Convenience and Accessibility: One of the most significant advantages of telemedicine is its convenience. Patients no longer need to take time off work, sit in waiting rooms, or travel long distances to see a doctor. With a computer or smartphone, consultations can happen from the comfort of home. This is especially beneficial for individuals living in rural or remote areas where access to healthcare facilities may be limited. Telemedicine breaks down geographical barriers, ensuring that more people have access to healthcare regardless of their location.
3. Cost-Effectiveness: Telemedicine has the potential to reduce healthcare costs for both patients and providers. For patients, virtual consultations often cost less than in-person visits, eliminating the need for travel expenses, parking fees, and taking time off work. For healthcare providers, telemedicine reduces overhead costs related to maintaining physical office spaces and allows for more efficient use of medical resources. This makes telemedicine an appealing option for patients with limited financial resources and for healthcare systems aiming to optimize efficiency.
4. Expanded Access to Specialists: Telemedicine enables patients to consult with specialists without the need to travel long distances or wait for months for an appointment. With telemedicine platforms, patients can access a wider pool of healthcare professionals, including those who may be located in different cities or even countries. This expanded access is especially valuable for patients who require specialized care for rare or complex conditions, where finding the right specialist locally might be challenging.
5. Telemedicine for Mental Health: Telemedicine has been particularly transformative in the field of mental health. Virtual therapy sessions have become increasingly popular, offering patients a convenient and private way to access mental health services. The stigma associated with seeking mental health support has made some individuals hesitant to seek help in person, but telemedicine offers a more private and less intimidating way to receive treatment. This has led to increased access to therapy and counseling services, which is vital as mental health issues continue to rise globally.
6. Challenges and Limitations: Despite its many benefits, telemedicine is not without its challenges. One of the most significant concerns is the digital divide, where certain populations lack access to reliable internet or the devices necessary for virtual healthcare. Privacy and security concerns regarding patient data are also a significant challenge, as telemedicine involves transmitting sensitive health information over the internet. Additionally, some healthcare services, such as physical exams, are difficult to conduct remotely, limiting the scope of telemedicine for certain medical conditions.
7. The Future of Telemedicine: As technology continues to evolve, so too will telemedicine. Future developments may include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance diagnosis, the use of remote monitoring devices to track patient health in real-time, and more sophisticated virtual consultations that can simulate in-person visits. Moreover, the ongoing push for telemedicine to become a permanent part of healthcare systems around the world, particularly in the wake of the pandemic, will likely lead to more widespread and equitable access to virtual care.
Conclusion: Telemedicine has proven itself to be a game-changer in the healthcare industry, offering a convenient, cost-effective, and accessible solution for patients and healthcare providers alike. While challenges remain, the rise of telemedicine represents a step toward more efficient and inclusive healthcare. As the technology continues to improve and expand, it is clear that virtual healthcare will play an increasingly important role in the future of medicine, offering a path toward more equitable, accessible, and efficient care.