The Hidden Impact of Stress: How Chronic Stress Affects Your Body and Mind
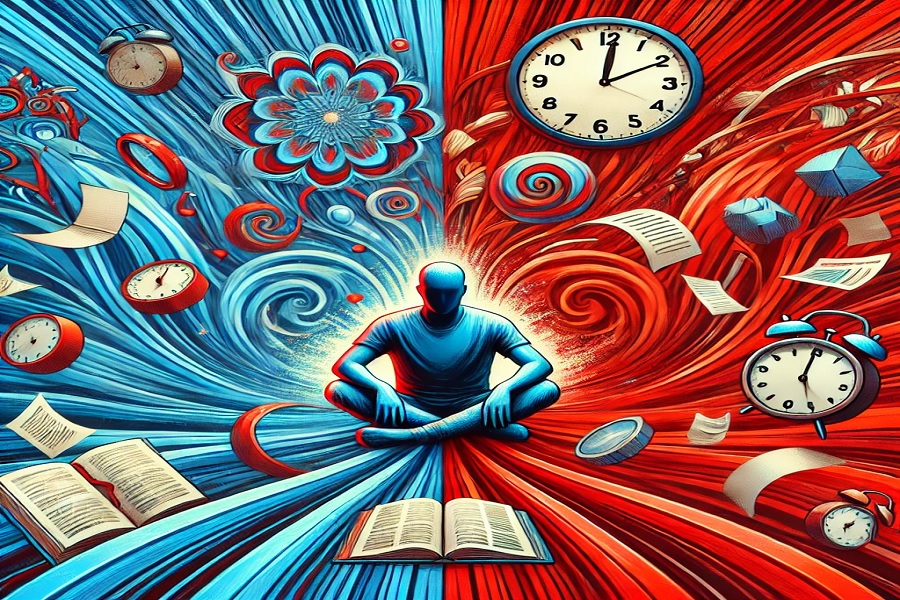

Stress is a natural part of life. It helps us react quickly in dangerous situations and adapt to challenges. However, when stress becomes chronic, it can have far-reaching consequences on both our physical and mental health. Understanding these hidden impacts is crucial to taking control of your well-being.
The Science Behind Stress
When faced with a stressful situation, the body activates its "fight or flight" response. This involves the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare the body to deal with immediate threats. While short bursts of these hormones can be beneficial, prolonged exposure can disrupt various systems in the body.
Physical Health Impacts
Cardiovascular Issues:
*Chronic stress can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, raising the risk of heart disease and stroke.
*It may also contribute to inflammation, a key factor in many chronic illnesses.
Weakened Immune System:
*Stress suppresses immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections and slower to heal.
Digestive Problems:
The gut-brain axis means stress can cause issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), indigestion, and ulcers.
Sleep Disorders:
Stress can lead to insomnia or poor-quality sleep, which exacerbates other health issues.
Chronic Pain:
Muscle tension and headaches are common physical manifestations of stress.
Mental Health Impacts
Anxiety and Depression:
Chronic stress can trigger or worsen anxiety and depressive disorders by altering brain chemistry and structure.
Cognitive Decline:
Stress affects memory and decision-making by impairing the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.
Emotional Instability:
Irritability, mood swings, and feelings of overwhelm are common emotional effects of chronic stress.
Behavioral Impacts
Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms:
Stress often leads to behaviors like overeating, smoking, or excessive alcohol consumption.
Reduced Productivity:
Difficulty concentrating and lack of motivation can hinder professional and personal growth.
Managing Stress Effectively
Mindfulness and Meditation:
Practices like deep breathing, yoga, and meditation help regulate stress responses and promote relaxation.
Physical Activity:
Regular exercise reduces cortisol levels and boosts endorphins, improving mood and resilience.
Balanced Diet:
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and antioxidants can mitigate the effects of stress.
Social Support:
Building strong relationships and talking about stressors can provide emotional relief.
Professional Help:
Therapy or counseling can be invaluable for learning stress-management strategies.
Conclusion
Chronic stress is more than just a mental burden; it is a pervasive issue that affects every aspect of our health. By recognizing its hidden impacts and taking proactive measures to manage it, we can reclaim our well-being and lead healthier, happier lives.






.jpg)